Download the ICM Software
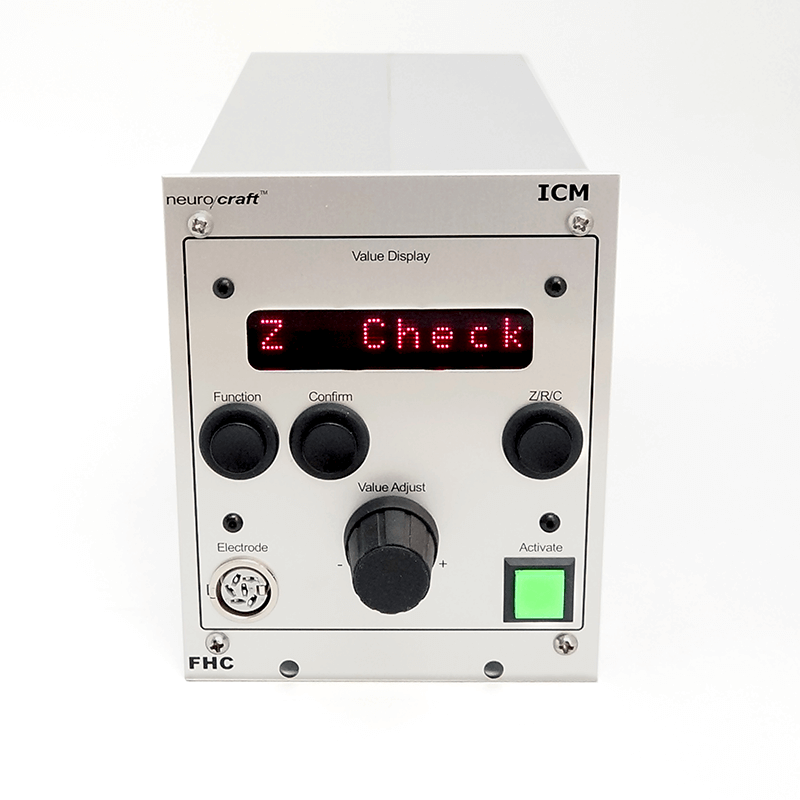
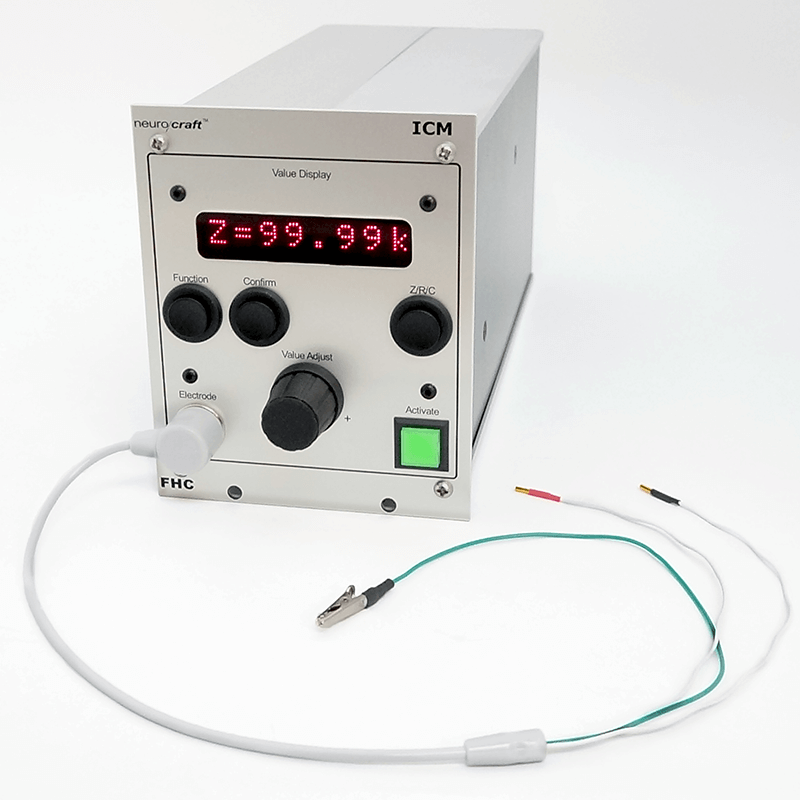
Technical Details:
- Measurement Accuracy: ±5% actual. Displayed to 2-3 digits, depending on range.
- Measurement Applied Voltage: Adjustable 10% – 100% of 1.75Vpp sine wave (Default is 20%)
- Measurement Frequency: Adjustable from 50Hz to 4kHz
- Impedance Range: 1kΩ to 100MΩ
- Conditioning Voltage Range: Adjustable 10% – 100% of 3.5Vpp sine wave (Default is 100%)
- Conditioning Current Frequency: Adjustable from 50Hz to 4kHz
- Display: 8 characters, 1cm height, red
- Power Requirements: 100-240 VAC, 50-60Hz
- Mounting Options: Tabletop, 4 rubber feet prevent sliding. Rack mountable with SAF Rack Frame
- Computer Interface: High-speed USB 2.0, backwards full-speed USB 1.1 compatible. (Computer needed for FLASH upgrade only)
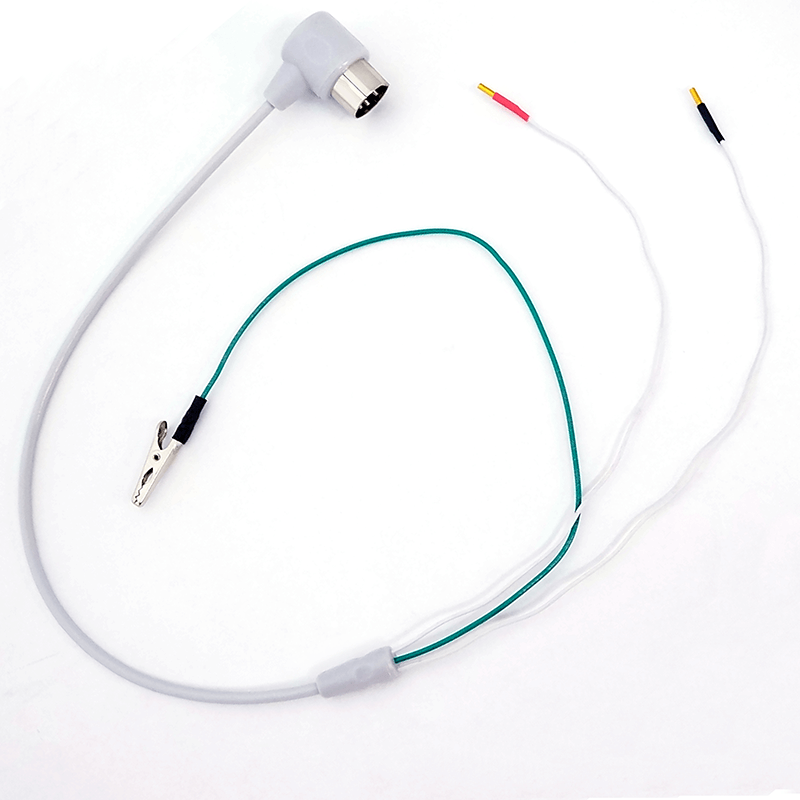
- Includes ICM Accessory Kit:
- Electrode Conditioning Cable, Rubber feet (use optional), Calibrated Test Loads, User Manual
Ordering Information:
Product number: 55-70-0
Included:
- ICM Module (55-70-0)
- Electrode Conditioning Cable
- Ruber Feet
- Calibrated test Loads
Product Sizes:
Dimensions:
- Height: 13cm (5.22in)
- Width: 10cm (4.20in)
- Length: 25cm (9.75in)
- Weight: 1.48 Kg (3.26 lbs)
Fiallos, A. M., Bricault, S. J., Cai, L. X., Worku, H. A., Colonnese, M. T., Westmeyer, G. G., & Jasanoff, A. (2017). Reward magnitude tracking by neural populations in ventral striatum. NeuroImage, 146, 1003–1015.
Go To Publication
Verhagen, J. V., Gabbott, P. L., & Rolls, E. T. (2003). A simple method for reconditioning epoxy-coated microelectrodes for extracellular single neuron recording. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 123(2), 215–217.
Go To Publication
Yogi A. Patel, Tarun Saxena, Ravi V. Bellamkonda & Robert J. Butera (2016) Kilohertz frequency nerve block enhances anti-inflammatory effects of vagus nerve stimulation. Scientific Reports,7:39810.
Go To Publication
Budai D, Vizvári AD, Bali ZK, Márki B, Nagy LV, et al. (2018) A novel carbon tipped single micro-optrode for combined optogenetics and electrophysiology. PLOS ONE 13(3): e0193836.
Go To Publication
Connolly, A. T., Vetter, R. J., Hetke, J. F., Teplitzky, B. A., Kipke, D. R., Pellinen, D. S., et al. (2016). A Novel Lead Design for Modulation and Sensing of Deep Brain Structures. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63(1), 148–157.
Go To Publication